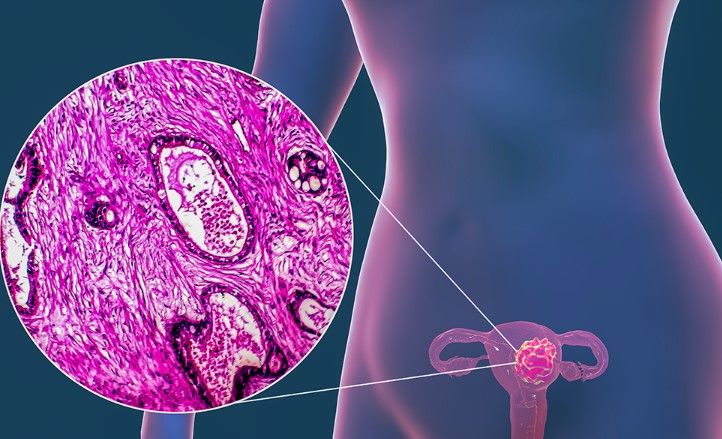
Understanding Cancer of the Uterus: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Cancer of the uterus, also known as uterine cancer, is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the uterus, the pear-shaped organ in a woman’s pelvis where fetal development occurs during pregnancy. Awareness of uterine cancer is crucial because early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and survival. Let’s dive into the details of this disease, exploring its types, causes, symptoms, treatments, and much more.
Types of Uterine Cancer
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is the most common type of uterine cancer, originating in the lining of the uterus known as the endometrium. It usually affects women after menopause, although younger women are not entirely exempt.
Uterine Sarcoma
Uterine sarcoma is much rarer and develops in the muscles or other tissues of the uterus. This type of cancer is more aggressive and often has a different treatment approach compared to endometrial cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predispositions
Certain genetic factors can increase the risk of uterine cancer. For instance, Lynch syndrome, a hereditary condition, raises the likelihood of developing this cancer.
Hormonal Imbalances
An imbalance of hormones, particularly estrogen, can stimulate the endometrium excessively, leading to cancerous changes. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and hormone replacement therapy can contribute to this imbalance.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, such as a high-fat diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity, can increase the risk of developing uterine cancer. Managing weight and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are crucial preventive measures.
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer
Early Signs
The early symptoms of uterine cancer often include abnormal vaginal bleeding, spotting, or discharge, especially after menopause. Women who experience these symptoms should seek medical advice promptly.
Advanced Symptoms
In more advanced stages, symptoms may include pelvic pain, a palpable mass, and unexplained weight loss. These signs indicate the cancer may have spread beyond the uterus.
Diagnosis
Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are the first steps in diagnosing uterine cancer. This includes discussing symptoms, family history, and conducting a pelvic exam.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests such as ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs help visualize the uterus and detect abnormalities.
Biopsy
A biopsy, where a small sample of endometrial tissue is taken for analysis, is crucial for confirming the presence of cancer cells.
Staging of Uterine Cancer
Stage I
Cancer is confined to the uterus.
Stage II
Cancer has spread to the cervix but not beyond the uterus.
Stage III
Cancer extends outside the uterus but remains within the pelvic area.
Stage IV
Cancer has spread to the bladder, bowel, or distant organs.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery, often involving the removal of the uterus (hysterectomy), is a primary treatment for uterine cancer. In some cases, the ovaries and fallopian tubes are also removed.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It can be used before surgery to shrink tumors or after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s often used when cancer has spread or if there’s a high risk of recurrence.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy blocks the hormones that fuel cancer growth, particularly in hormone-sensitive cancers.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances to precisely identify and attack cancer cells without harming normal cells. This treatment is based on specific genetic markers of the cancer.
Side Effects of Treatments
Common Side Effects
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and skin changes. Each treatment type has its own specific side effects.
Managing Side Effects
Managing side effects involves a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, and support from healthcare providers to maintain quality of life during treatment.
Prevention and Early Detection
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of uterine cancer. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking.
Regular Screenings
Regular pelvic exams and reporting any unusual symptoms promptly can aid in early detection and improve treatment outcomes.
Living with Uterine Cancer
Coping Strategies
Coping with a uterine cancer diagnosis involves emotional and psychological support. Joining support groups and counseling can be beneficial.
Support Systems
Family, friends, and healthcare teams form an essential support system for those living with uterine cancer. Their support can make a significant difference in managing the disease.
Diet and Nutrition
Foods to Eat
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports overall health and recovery during treatment.
Foods to Avoid
Avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar, and high-fat diets can help manage weight and reduce cancer recurrence risk.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Benefits of Exercise
Regular physical activity helps improve mood, energy levels, and overall health. It can also help manage treatment side effects.
Recommended Activities
Activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga are gentle yet effective ways to stay active during and after cancer treatment.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Dealing with Diagnosis
Receiving a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Seeking emotional support from mental health professionals, support groups, and loved ones is crucial.
Mental Health Support
Ongoing mental health support, including therapy and counseling, can help manage anxiety, depression, and other emotional challenges associated with cancer.
Research and Advances in Uterine Cancer
Latest Studies
Recent studies focus on improving early detection methods and developing more effective, less invasive treatments.
Promising Treatments
Advances in immunotherapy and personalized medicine are showing promise in treating uterine cancer more effectively.
Conclusion
Uterine cancer, while serious, is treatable, especially when detected early. Awareness, regular screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices play crucial roles in prevention and early detection. Staying informed and seeking support can empower those affected to navigate their journey with resilience.
FAQs
What is the most common type of uterine cancer?
Endometrial cancer is the most common type, originating in the lining of the uterus.
Can uterine cancer be prevented?
While not all cases can be prevented, a healthy lifestyle and regular screenings can significantly reduce the risk.
What are the survival rates for uterine cancer?
Survival rates vary by stage at diagnosis, but early-stage uterine cancer has a high survival rate with appropriate treatment.
How does hormonal therapy work for uterine cancer?
Hormonal therapy works by blocking hormones that fuel the growth of certain types of uterine cancer.
What should I ask my doctor if I am diagnosed with uterine cancer?
Ask about the type and stage of cancer, treatment options, potential side effects, and support resources available to you.
You May Also Like

Understanding Blindness: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
December 1, 2024
Understanding Bladder Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
July 1, 2024