Understanding Blindness: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Introduction to Blindness
Blindness, a severe visual impairment, is a condition that profoundly affects an individual’s ability to perform everyday activities. It can be caused by a myriad of factors, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental influences. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various causes, symptoms, and management strategies for blindness, offering a detailed overview for those seeking to understand and mitigate the impact of this condition.
Types of Blindness
Total Blindness
Total blindness, also known as no light perception (NLP), refers to the complete lack of form and visual light perception. Individuals with total blindness cannot see any light or shapes and rely entirely on other senses for navigation and communication.
Partial Blindness
Partial blindness, or low vision, encompasses a spectrum of visual impairments that do not qualify as complete blindness. This includes conditions where individuals have limited vision, such as the ability to perceive light, colors, or shapes, but not enough to perform everyday tasks without assistance.
Common Causes of Blindness
Genetic Disorders
Genetic disorders are a significant cause of blindness. Conditions such as retinitis pigmentosa, Leber’s congenital amaurosis, and certain types of albinism are inherited and lead to progressive vision loss over time.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
AMD is a leading cause of blindness in individuals over the age of 50. This condition affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision, leading to a gradual loss of central vision.
Cataracts
Cataracts occur when the lens of the eye becomes clouded, causing blurred vision. While cataracts can often be treated with surgery, they remain a leading cause of blindness, particularly in developing countries where access to medical care is limited.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that damage the optic nerve, often due to high intraocular pressure. This damage is progressive and can lead to irreversible blindness if not managed appropriately.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy results from damage to the blood vessels in the retina caused by high blood sugar levels. This condition is a common complication of diabetes and can lead to blindness if not properly managed.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Recognizing Symptoms
Early detection of visual impairment is crucial for preventing blindness. Common symptoms include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Difficulty seeing in low light conditions
- Loss of peripheral vision
- Seeing flashes of light or floating spots
Regular Eye Examinations
Regular eye examinations are essential for early detection of conditions that can lead to blindness. Ophthalmologists can identify signs of eye diseases early, allowing for timely intervention and management.
Management and Treatment Options
Medical Interventions
Surgical Procedures
- Cataract Surgery: A common and effective procedure to restore vision in individuals with cataracts.
- Laser Surgery: Used to treat diabetic retinopathy and certain types of glaucoma.
Medications
- Eye Drops: Used to manage glaucoma by reducing intraocular pressure.
- Anti-VEGF Therapy: Injections used to treat wet age-related macular degeneration by inhibiting abnormal blood vessel growth.
Assistive Technologies
Advancements in technology have led to the development of various assistive devices for individuals with blindness, including:
- Screen Readers: Software that converts text on a screen into speech or Braille.
- Magnifying Devices: Electronic or optical devices that enlarge text and images for better visibility.
Rehabilitation Programs
Rehabilitation programs are essential for helping individuals with blindness adapt to their condition and maintain independence. These programs may include:
- Orientation and Mobility Training: Teaching navigation skills using a white cane or guide dog.
- Braille Literacy: Instruction in reading and writing Braille for effective communication.
Preventive Measures
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of developing conditions that lead to blindness. This includes:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Regular Exercise: Promoting overall health and reducing the risk of diabetes and hypertension.
Protective Eyewear
Wearing protective eyewear can prevent injuries that may lead to blindness. This is particularly important in environments with potential hazards, such as construction sites or when participating in sports.
Managing Chronic Conditions
Effective management of chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension is crucial in preventing complications that can lead to blindness. Regular check-ups and adherence to prescribed treatments are essential.
Living with Blindness
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with blindness can be challenging, and emotional and psychological support is vital. Counseling and support groups provide a platform for individuals to share experiences and coping strategies.
Community and Support Networks
Building a strong support network is crucial for individuals with blindness. Community organizations and advocacy groups offer resources, advocacy, and social connections that enhance the quality of life.
Education and Employment
Access to education and employment opportunities is essential for individuals with blindness. Inclusive education systems and workplace accommodations enable individuals to achieve their full potential.
Conclusion
Blindness, while challenging, is a condition that can be managed with the right knowledge, support, and resources. Early detection, medical intervention, and a supportive environment are key to improving the quality of life for individuals with blindness. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies, we can work towards a more inclusive and supportive society for those affected by this condition.
You May Also Like
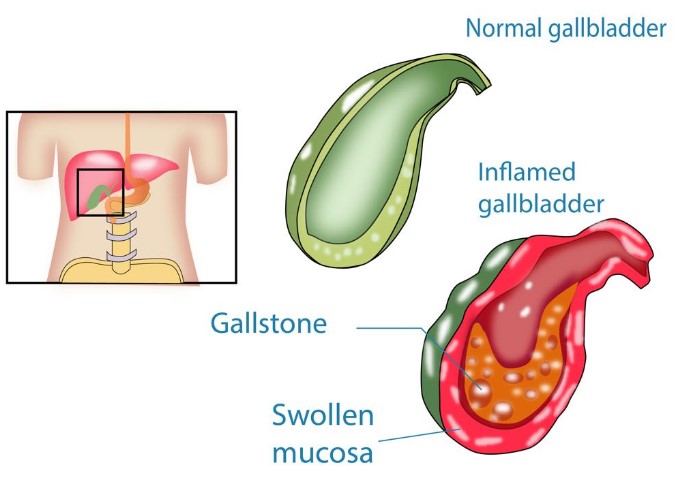
Cholecystitis (Gallbladder Inflammation)
May 26, 2024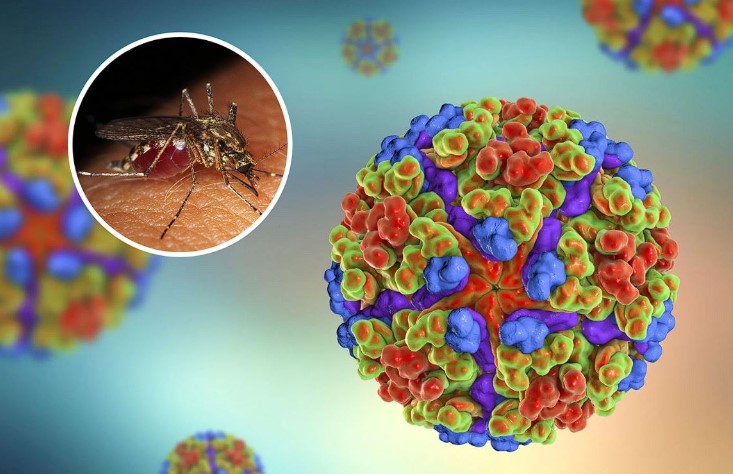
Understanding the Chikungunya Virus: Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
December 26, 2023