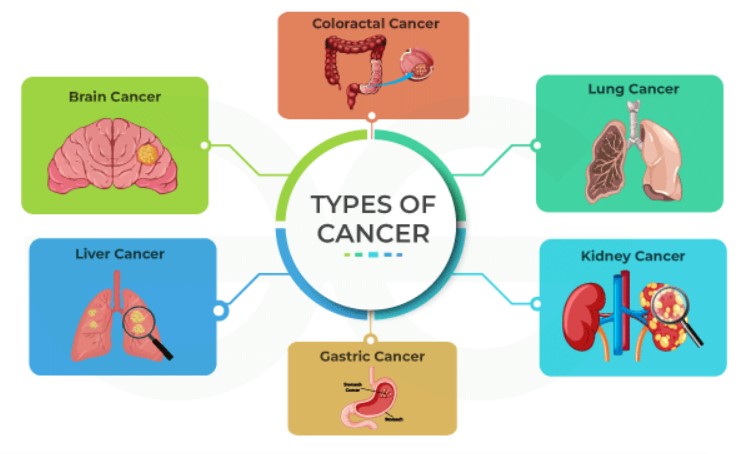
Understanding the Different Types of Cancer
Introduction
Cancer. Just hearing the word can bring a wave of emotions. It’s a term that encompasses a wide range of diseases, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. At its core, cancer involves the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body, which can invade and destroy normal tissue. Understanding the different types of cancer is crucial not only for patients and their families but for anyone who wants to be proactive about their health. Let’s delve into the diverse world of cancer types, their characteristics, and what we can do about them.
Common Cancer Types
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women worldwide. It occurs when cells in the breast grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Early detection through self-exams and mammograms can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment. Symptoms often include lumps in the breast, changes in breast shape, and discharge from the nipple.
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, often linked to smoking, affects the lungs’ ability to function properly. There are two main types: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Symptoms may include a persistent cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Early detection is challenging but crucial for better outcomes.
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer affects the prostate gland in men and is one of the most common cancers in men. Symptoms can include difficulty urinating, blood in urine, and pelvic discomfort. Regular screening, such as PSA tests, can help detect prostate cancer early.
Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer starts in the colon or rectum and is often preceded by polyps, which can be detected and removed during colonoscopy screenings. Symptoms might include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, and abdominal discomfort.
Rare Cancer Types
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is known for its low survival rate due to late detection. It affects the pancreas, an organ that helps with digestion and blood sugar regulation. Symptoms are often vague, including jaundice, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It leads to the production of abnormal white blood cells. Symptoms can include frequent infections, fatigue, and easy bruising or bleeding.
Lymphoma
Lymphoma starts in the lymphatic system, part of the body’s germ-fighting network. The two main types are Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Symptoms may include swollen lymph nodes, fever, and night sweats.
Liver Cancer
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, primarily affects people with underlying liver disease such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, weight loss, and jaundice.
Gender-Specific Cancers
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer affects the cervix in women and is often linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Regular Pap smears can detect precancerous changes in the cervix, allowing for early intervention.
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer starts in the ovaries and is often diagnosed at a late stage due to subtle symptoms like bloating, pelvic pain, and changes in bowel habits. Regular pelvic examinations and awareness of family history are important for early detection.
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer affects the testicles and is most common in younger men. Symptoms include lumps or swelling in the testicles and a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum. Regular self-exams can aid in early detection.
Skin Cancers
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, arising from the pigment-producing cells called melanocytes. It can develop anywhere on the body, often in areas exposed to the sun. Early signs include changes in moles’ size, shape, or color.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common but least dangerous form of skin cancer. It typically appears as a pearly bump or a flesh-colored mole. BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads but can cause significant local damage if untreated.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arises from the squamous cells in the skin. It often appears as a red, scaly patch or a sore that doesn’t heal. While more aggressive than BCC, it can usually be treated effectively if caught early.
Childhood Cancers
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma is a cancer that develops from immature nerve cells and mostly affects children under the age of 5. Symptoms may include abdominal swelling, bone pain, and a general feeling of illness.
Wilms Tumor
Wilms tumor is a type of kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Symptoms can include an abdominal mass, abdominal pain, fever, and blood in the urine. It is usually treatable with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare eye cancer that typically affects young children. It often presents as a white glow in the pupil when light is shone into the eye. Early detection is crucial for preserving vision and preventing the spread of the cancer.
Brain and Spinal Cord Cancers
Glioblastoma
Glioblastoma is an aggressive type of brain cancer. Symptoms can include headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits. Despite advances in treatment, it remains one of the most challenging cancers to treat.
Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma is a type of cancer that can occur in the brain or spinal cord. It arises from star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes. Symptoms depend on the tumor’s location and can include headaches, seizures, and cognitive difficulties.
Meningioma
Meningioma is a tumor that forms on the meninges, the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign, but they can cause significant issues if they press on vital brain structures.
Genetic and Lifestyle Factors in Cancer Development
Hereditary Cancers
Some cancers run in families due to inherited genetic mutations. Examples include BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations linked to breast and ovarian cancers. Knowing your family history can help with early detection and prevention strategies.
Lifestyle-Related Cancers
Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk of various cancers. Adopting healthier habits can significantly reduce this risk.
Diagnosis and Screening
Early Detection Methods
Early detection is key to improving cancer outcomes. Methods include mammograms, Pap smears, colonoscopies, and low-dose CT scans. Regular screenings can catch cancers before they become advanced.
Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools like biopsies, imaging tests (MRI, CT scans, PET scans), and blood tests help doctors determine the type, stage, and extent of cancer. Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment planning.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for many solid tumors. It involves removing the tumor and, in some cases, nearby tissues or lymph nodes to prevent the spread of cancer.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments. Side effects vary depending on the treatment area.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be systemic, affecting the entire body, or localized. While effective, it often comes with side effects like nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy aims at specific molecules involved in cancer growth. By targeting these molecules, this treatment can be more effective and less harmful to normal cells compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer. It includes treatments like checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy. This innovative approach has shown promise in treating various cancers.
Living with Cancer
Managing Symptoms and Side Effects
Living with cancer often involves managing symptoms and side effects from both the disease and its treatment. This can include pain management, nutritional support, and dealing with fatigue and emotional stress.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Cancer diagnosis and treatment can take a significant emotional toll. Support from family, friends, counselors, and support groups is vital. Mental health care, including therapy and medication, can also play a crucial role.
Preventive Measures
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing cancer. This includes eating a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol.
Vaccinations
Vaccines like the HPV vaccine can prevent cancers caused by infections. The hepatitis B vaccine can reduce the risk of liver cancer. Vaccination is a simple yet effective preventive measure.
Regular Screenings
Regular screenings are essential for early detection of cancers. Following guidelines for screenings based on age, gender, and risk factors can catch cancers in their early, more treatable stages.
Recent Advances in Cancer Research
Breakthrough Therapies
Recent years have seen significant advances in cancer treatment. Breakthroughs like personalized medicine and gene editing hold promise for more effective and less toxic treatments.
Emerging Technologies
Technologies such as liquid biopsies, which detect cancer DNA in blood, and advanced imaging techniques are revolutionizing cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are critical for testing new treatments. Participating in trials can provide access to cutting-edge therapies and contribute to medical research.
Support Systems for Cancer Patients
Support Groups
Support groups offer a sense of community and shared experiences for cancer patients. They provide emotional support, practical advice, and a place to share stories and strategies.
Counseling Services
Professional counseling can help patients and their families cope with the emotional aspects of cancer. Therapy can provide strategies for dealing with anxiety, depression, and stress.
Online Resources
Numerous online resources provide information, support, and community for cancer patients. Websites, forums, and social media groups can offer valuable insights and connections.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of cancer is the first step in fighting this complex disease. Awareness, early detection, and advances in treatment offer hope and a brighter future for those affected by cancer. By staying informed and proactive, we can improve outcomes and support those on their cancer journey.
FAQs
What are the most common symptoms of cancer?
Common symptoms include unexplained weight loss, fatigue, lumps or swelling, persistent pain, and changes in bowel or bladder habits. However, symptoms vary widely depending on the type of cancer.
Can cancer be prevented?
While not all cancers can be prevented, reducing risk factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can lower the risk of many cancers.
How is cancer staged?
Cancer staging involves determining the extent of cancer spread. Stages range from 0 (in situ) to IV (advanced/metastatic), based on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and metastasis.
What is the role of genetics in cancer?
Genetics can play a significant role in cancer development. Some cancers are linked to inherited genetic mutations. Genetic testing can help identify individuals at higher risk.
Are there any natural treatments for cancer?
While some natural remedies may help with symptom management, they should not replace conventional treatments. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative therapies.
You May Also Like

Understanding Blepharospasm: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
November 1, 2024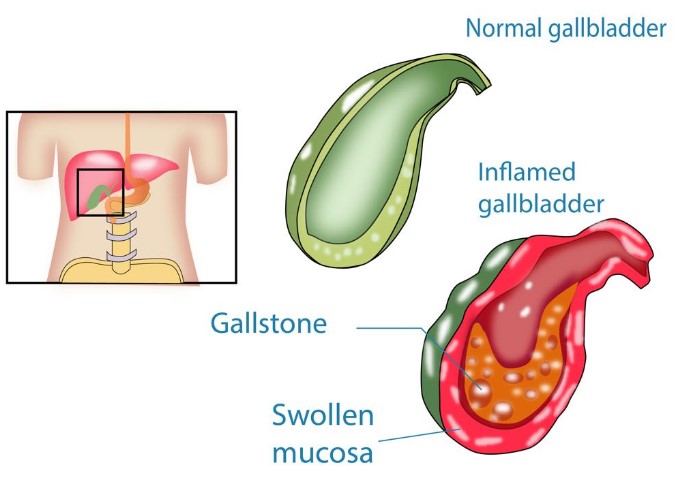
Cholecystitis (Gallbladder Inflammation)
May 26, 2024