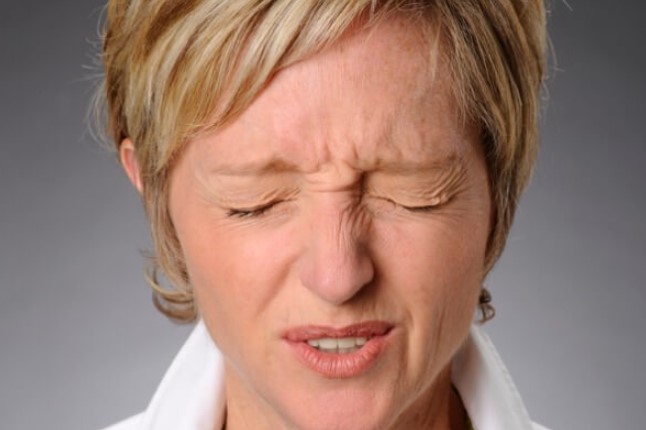
Understanding Blepharospasm: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Blepharospasm is a neurological condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions around the eyes, leading to excessive blinking and eyelid closure. This condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into every aspect of blepharospasm to provide you with a thorough understanding of this condition.
What is Blepharospasm?
Blepharospasm is classified as a type of dystonia, which is a movement disorder that causes muscles to contract uncontrollably. Specifically, blepharospasm affects the orbicularis oculi muscle, resulting in repeated, uncontrollable blinking and eyelid spasms. These spasms can be mild or severe, with some individuals experiencing the complete closure of the eyelids for extended periods, rendering them functionally blind.
Causes of Blepharospasm
The exact cause of blepharospasm remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
1. Genetic Predisposition
Research suggests that a genetic component may play a role in the onset of blepharospasm. Individuals with a family history of dystonia or other movement disorders may be at a higher risk of developing blepharospasm.
2. Environmental Triggers
Certain environmental factors can trigger or exacerbate blepharospasm. These may include:
- Stress and Fatigue: High levels of stress and physical exhaustion can worsen symptoms.
- Eye Irritation: Conditions such as dry eyes, conjunctivitis, or blepharitis can contribute to the onset of blepharospasm.
- Exposure to Bright Lights: Sensitivity to light, or photophobia, is a common trigger for blepharospasm.
3. Neurological Factors
Blepharospasm is often associated with abnormalities in the basal ganglia, a part of the brain responsible for controlling movement. Dysfunction in this area can lead to the involuntary muscle contractions seen in blepharospasm.
4. Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, particularly those affecting the central nervous system, can induce blepharospasm as a side effect. These may include drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease, antipsychotics, and some antidepressants.
Symptoms of Blepharospasm
The symptoms of blepharospasm can vary in severity and may include:
1. Excessive Blinking
One of the earliest signs of blepharospasm is increased blinking, which may progress to more severe spasms.
2. Involuntary Eyelid Closure
In advanced cases, the eyelids may close involuntarily for seconds to minutes, impairing vision.
3. Eye Irritation and Dryness
Patients often report a sensation of grittiness or dryness in the eyes, which can exacerbate blinking and spasms.
4. Sensitivity to Light
Photophobia, or sensitivity to light, is a common symptom that can trigger or worsen blepharospasm episodes.
5. Facial Twitches
In some cases, muscle spasms may extend to other parts of the face, causing twitches or grimacing.
Diagnosis of Blepharospasm
Diagnosing blepharospasm involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Neurologists may also use specialized tests to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis:
1. Clinical Evaluation
A comprehensive clinical evaluation includes a detailed patient history and observation of symptoms. Doctors look for characteristic signs of blepharospasm, such as excessive blinking and involuntary eyelid closure.
2. Electromyography (EMG)
EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles and can help confirm the presence of muscle spasms and rule out other neuromuscular disorders.
3. Imaging Studies
In some cases, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans may be performed to rule out structural brain abnormalities that could be causing symptoms.
Treatment Options for Blepharospasm
While there is no cure for blepharospasm, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
1. Botulinum Toxin Injections
Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections are the most common and effective treatment for blepharospasm. The toxin temporarily paralyzes the muscles responsible for spasms, providing relief for several months before repeat injections are necessary.
2. Medications
Oral medications such as anticholinergics, muscle relaxants, and benzodiazepines may be prescribed to reduce muscle spasms. However, their effectiveness varies, and they often come with side effects.
3. Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, surgical options such as myectomy (removal of some eyelid muscles) or deep brain stimulation (DBS) may be considered. These procedures aim to reduce the frequency and severity of spasms.
4. Supportive Therapies
Supportive therapies such as physical therapy, biofeedback, and stress management techniques can also help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference in managing blepharospasm symptoms. These include:
- Wearing Sunglasses: To reduce light sensitivity and protect the eyes from irritation.
- Practicing Good Sleep Hygiene: Ensuring adequate rest and reducing fatigue.
- Using Lubricating Eye Drops: To alleviate dryness and irritation.
Living with Blepharospasm
Living with blepharospasm can be challenging, but with proper management and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Joining support groups and connecting with others who have the condition can provide valuable emotional support and practical advice.
1. Psychological Impact
Blepharospasm can significantly impact mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Seeking counseling or therapy can help address these issues and improve coping strategies.
2. Workplace Accommodations
For those affected by blepharospasm, workplace accommodations such as flexible schedules, reduced screen time, and ergonomic adjustments can make a significant difference in maintaining employment and productivity.
3. Advocacy and Awareness
Raising awareness about blepharospasm can help reduce stigma and promote understanding of the condition. Advocacy efforts can also support research into better treatments and potential cures.
Conclusion
Blepharospasm is a complex neurological condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for those affected by this condition. While there is currently no cure, various therapies and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of blepharospasm, seeking medical advice and support is essential.
You May Also Like

Bleeding After Menopause
September 1, 2024
Childhood Illnesses
February 20, 2024